
Causes of labial papilloma

- The presence of HPV in the body;
- Decreased protective functions of the body;
- Women don't care about their health.
notes!Men, although carriers of the disease, are much less likely to develop lesions in the anogenital area. The reason is also that the special structure of female reproductive organs is more prone to micro-cracks, which leads to a decrease in local protective function.
Symptoms of labial papilloma
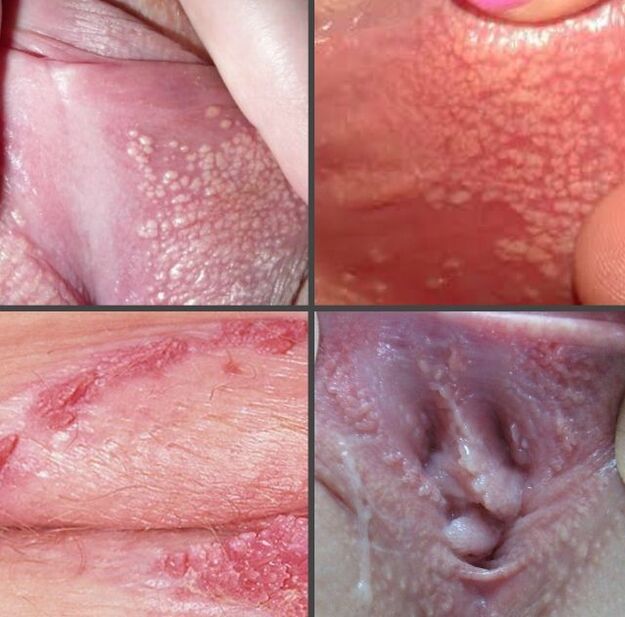
- unit formation- Small flesh-colored seal, rarely exceeding 6 mm in diameter.
- Various structures, these structures resemble cockcombs in appearance. This growth is evidence of advanced disease. If the formations are damaged during standard sanitation procedures, their color may change from flesh-colored to dark brown.
Self-study of photos of labial papilloma and identification of similar structures does not eliminate the need to see a doctor. Only a thorough diagnosis will help determine the true cause of the disease and determine the best treatment.
- Blood and urine to assess general health;
- Take a tissue biopsy of the established growth;
- PCR tests and Digen tests are narrow-spectrum tests used to confirm the presence of the virus in the body and identify its strain.
notes!Papillomas on the labia may arise under the simultaneous influence of multiple viral strains, some of which are carcinogenic (16, 18, 33, etc. ). Only a complete examination can help identify all active genotypes.
How to treat labial papilloma
Drugs to Treat Labial Papilloma
- antiviral drugs, inhibit the growth of pathogenic microorganisms.
- immunomodulator, thanks to synthetic elements, it helps the immune system perform its tasks.
- immune boosterHelps the immune system function.
notes!There is no single medical treatment for labial papilloma. Doctors select drugs, dosages and combinations individually based on the patient's specific situation.
Removal of papillomas on the labia

- current- A rather painful but doable method that has proven itself over the years.
- freeze damage—Removal of formations under the influence of low temperatures.
- laser— Advanced technology allows you to painlessly remove growths using high temperatures.
- radio knife- The most modern method uses directed radio waves to remove papillomas on the labia.
notes!All of the listed methods can be used to remove papillomas on the outer and inner labia. However, in view of the greater sensitivity of the labia minora mucosa, it is best to choose laser or radio knife to destroy it at this location.
Traditional medicine against labial papilloma

- Unless otherwise stated in the formula, the composition must be prepared immediately before application to growth;
- Do not exceed the dose stated on the prescription;
- If you experience a burning sensation when using the product, or if the papilloma begins to grow or deform, you must stop self-medication and consult a doctor;
- If the papilloma does not disappear within the specified time, you must seek expert help.
important!The difficulty in calculating drug concentrations is why most doctors do not support the use of conventional medical methods to treat labial papillomas. Increased doses of active substances can lead to irritation of adjacent healthy tissue.
Preventive measures for labial papillomas
- Follow personal hygiene rules;
- Quit bad habits and promiscuity;
- Proper nutrition and moderate exercise;
- preventive check-ups by doctors;
- Refuse to self-treat papillomas elsewhere in the body.























